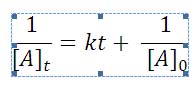
Second Order Reaction and Rate Law:
Section 14.3, pg. 560, Burge.
A second order rate law means that the rate of reaction depends on the concentration of two reactants raised to the first reaction, or one reaction raised to the second power.
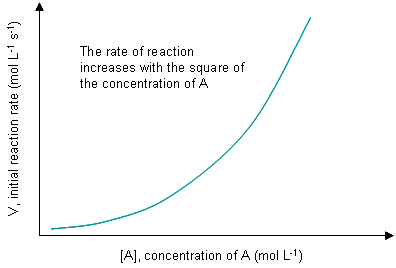
The graph of the reaction rate with respect to initial concentration shows that it is an exponential function such that the rate increases by the square of the concentration of the reaction, [A]2.

The graph of the reaction rate with respect to the reciprocal concentration is a linear function where at the the reciprocal of highest concentrations appear as the smallest number, and as the concentration drops, the reciprocal gets larger.
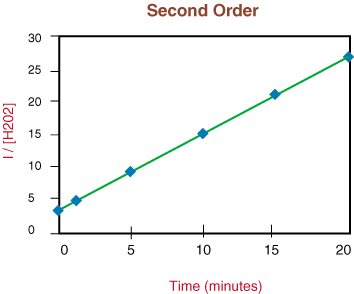
This gives a linear function where the reaction rate can be experimentally determined by taking the slope of the line in the form of y= mx + b.
The integrated rate law for a order reaction is given here without derivation: